By NutriLife Team | October 26, 2023
Exploring the Fascinating Link Between Your Gut and Your Mind
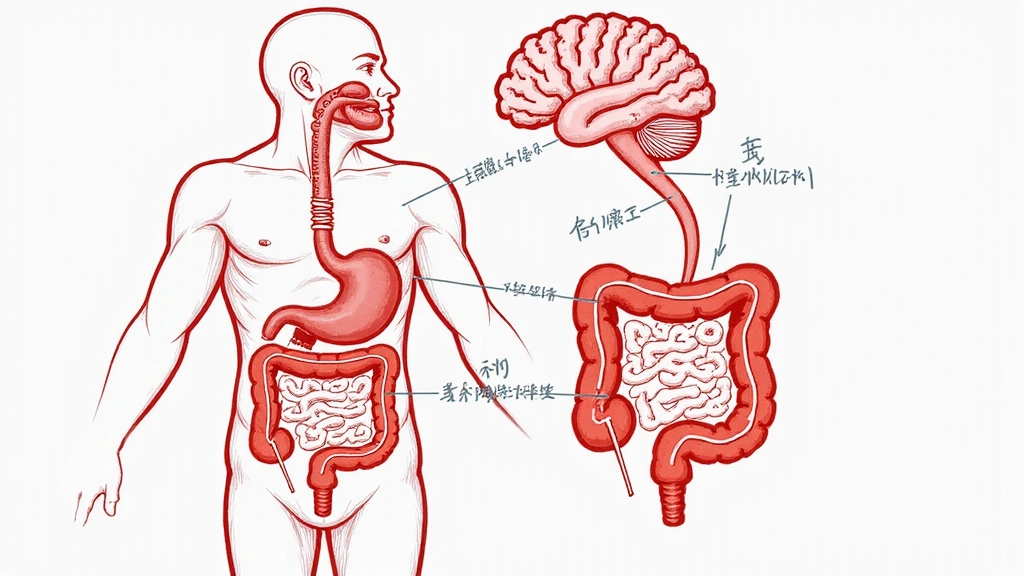
Did you know that your gut is often referred to as your "second brain"? This isn't just a catchy phrase; it reflects a profound and bidirectional communication system known as the gut-brain axis. This intricate network involves the central nervous system, the enteric nervous system (which governs your gut), and the trillions of microorganisms residing in your digestive tract – your gut microbiome.
What is the Gut-Brain Axis?
The gut-brain axis is a complex communication system that links your gut to your brain. It's not just a one-way street; signals travel in both directions, influencing everything from your mood and cognitive function to your immune system and overall physical health. Key players in this communication include the vagus nerve, neurotransmitters produced in the gut, and immune system chemicals.
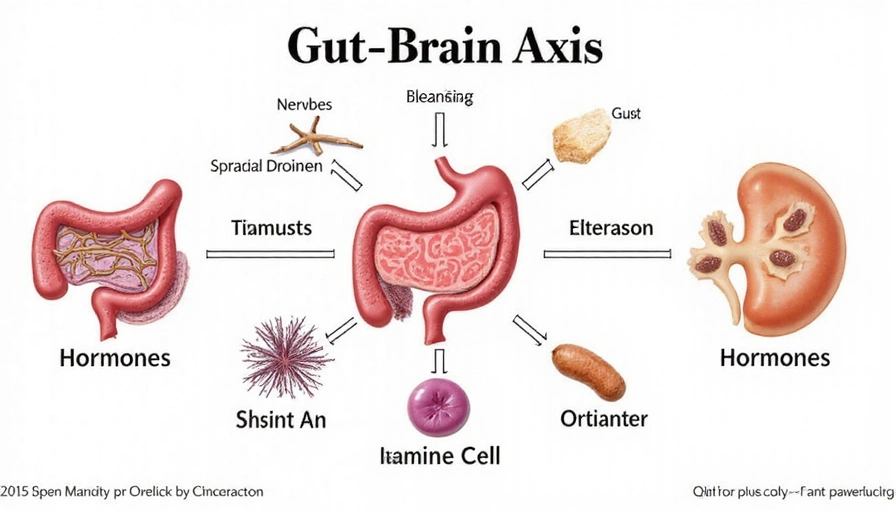
The Role of the Gut Microbiome
Your gut microbiome, a diverse community of bacteria, fungi, and viruses, plays a pivotal role in this axis. These microorganisms produce a variety of compounds, including short-chain fatty acids and neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine, which can directly affect brain function and mood. An imbalance in your gut flora, known as dysbiosis, has been linked to various mental health conditions, including anxiety and depression.
How Diet Impacts the Gut-Brain Connection
What you eat directly influences the health of your gut microbiome, and by extension, your brain. A diet rich in fiber, fermented foods, and probiotics can foster a diverse and healthy gut environment. Conversely, a diet high in processed foods, sugar, and unhealthy fats can lead to inflammation and dysbiosis, negatively impacting your mental well-being.
- Probiotics: Found in yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi, these introduce beneficial bacteria.
- Prebiotics: Found in garlic, onions, bananas, and oats, these nourish existing good bacteria.
- Fiber-rich foods: Whole grains, fruits, and vegetables support a diverse microbiome.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, these have anti-inflammatory properties beneficial for both gut and brain.
Practical Steps to Nurture Your Gut-Brain Health
Taking care of your gut is a powerful way to support your mental health. Here are some actionable steps you can take:
- Eat a diverse, whole-food diet: Focus on plant-based foods, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Include fermented foods: Regularly consume yogurt, kimchi, or kombucha.
- Manage stress: Stress can negatively impact your gut. Practices like meditation, yoga, and deep breathing can help.
- Prioritize sleep: Adequate sleep is crucial for both gut and brain health.
- Stay active: Regular physical activity has been shown to positively influence gut microbiota diversity.
The gut-brain connection is a fascinating and rapidly evolving area of research. By understanding and nurturing this vital link, you can significantly improve your overall health and well-being. At NutriLife Indonesia, we believe in a holistic approach to nutrition, recognizing that true health encompasses both body and mind. Stay tuned for more insights into how nutrition can transform your life!
Comments
Commenting system placeholder (e.g., Disqus integration or custom form).